Olive oil acidity is a crucial indicator of quality, measured by the percentage of free fatty acids present, primarily oleic acid. Extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) must have an acidity level of 0.8% or less, while virgin olive oil can have up to 2% acidity. Lower acidity generally indicates higher quality oil, as it suggests the olives were fresh and properly handled during processing.
Olive Acidity Definition
Olive oil acidity is a measure of the free fatty acid (FFA) content in the oil, expressed as a percentage of oleic acid. It indicates the breakdown of triglycerides into free fatty acids due to enzymatic activity or poor handling of olives before extraction. The lower the acidity, the higher the quality of the oil.
The acidity of olive oil does not directly affect its taste or nutritional composition. However, lower acidity is associated with higher levels of beneficial compounds such as antioxidants, particularly oleic acid and polyphenols. These compounds help combat inflammation and oxidative stress in the body, contributing to the oil’s health benefits.
Higher Acidity Suggests Lower Quality
The higher acidity in olive oil is not inherently harmful to health, but it does indicate lower quality oil that may have undergone degradation or been produced from damaged olives. Oils with higher acidity tend to have a shorter shelf life and may lose their beneficial properties more quickly. Lower acidity usually means better quality, suggesting the olives were fresh and properly handled before extraction.
When it comes to health effects, choosing lower-acidity olive oil (such as EVOO) is generally recommended. These oils retain more of their antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties, which are associated with various health benefits, including heart health. Many people associate the acidity of olive oil with the intensity of its flavor, but this is a misconception.
Percentage & Quality Levels
By looking only at the acidity of olive oils in the different categories, we can distinguish:
- Olive oil: it has a maximum acidity level of 1.5%. This oil is marketed as “mild” or “intense”, but you should bear in mind that most of it has a high percentage of refined oil.
- Virgin olive oil: the degree of acidity is usually above 0.8%, and should not exceed 2%.
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO): has a maximum acidity of 0.8%. This is the main difference between virgin and extra virgin olive oil.
Premium EVOO and Acidity Levels
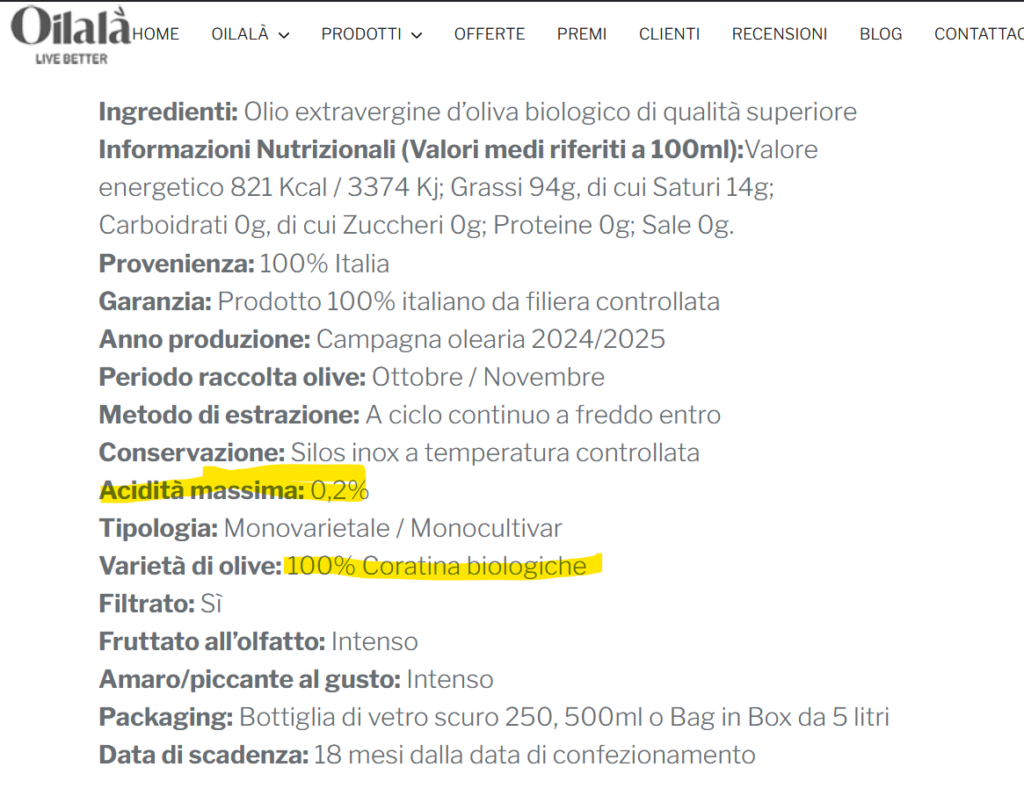
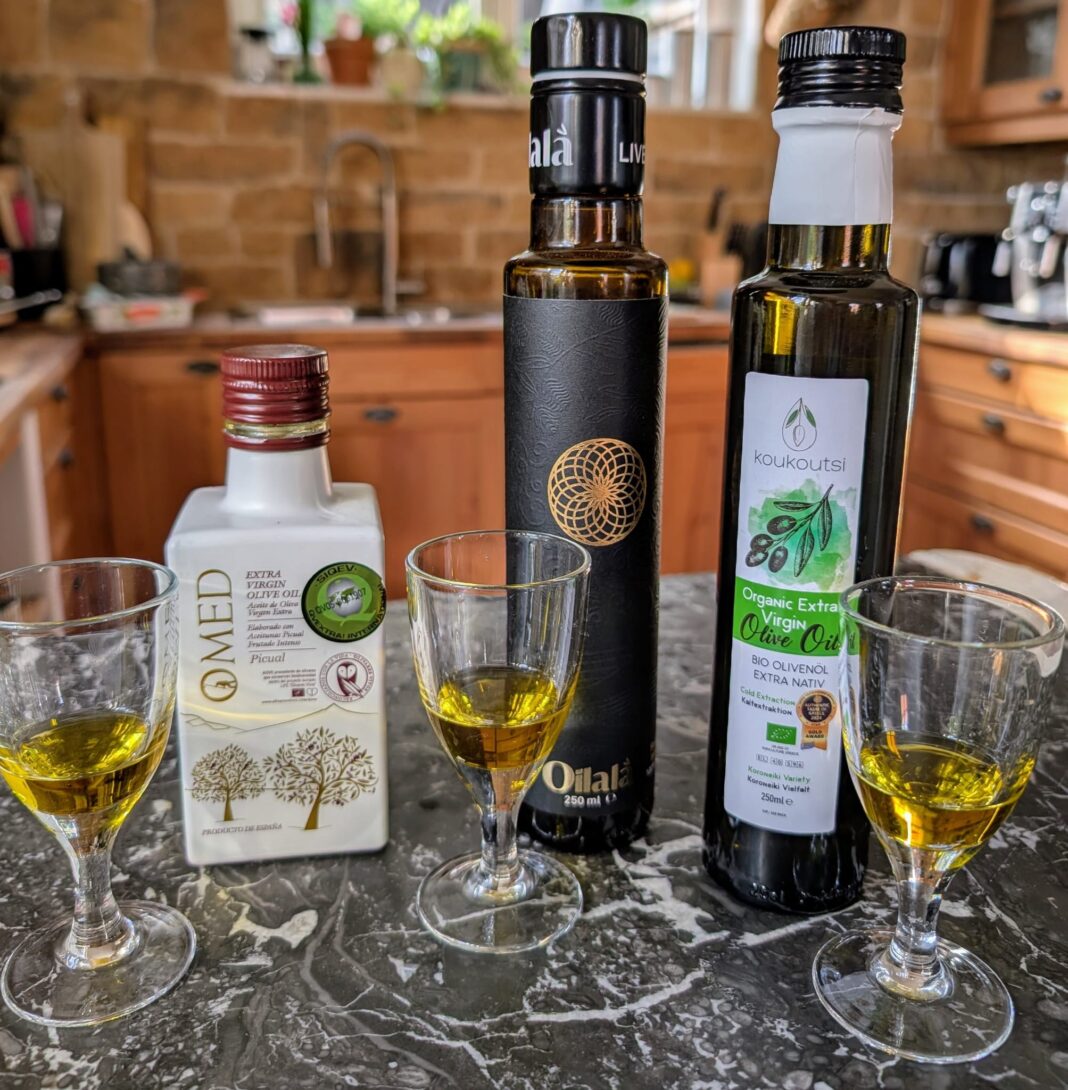
For example, the Spanish Picual EVOO from O-Med (link) has an oleic acid content of 0.1%, the Italian organic Coratina EVOO from Oilala (link) has a maximum content of 0.2%, and the organic Greek Organic Extra Virgin from Koukoutsi (link) has 0.3%.
While the fatty acid composition remains relatively constant regardless of acidity, lower acidity oils are likely to provide more beneficial nutrients due to their superior production process.
In conclusion, while higher acidity in olive oil is not directly harmful, it is an indicator of lower quality. For optimal health benefits and flavor, consumers should opt for extra virgin olive oil with low acidity levels, ideally below 0.3%. Lower levels of free fatty acids mean better flavor and more health benefits. So next time you’re shopping for olive oil, pay attention to its acidity!
To keep your olive oil fresh and low in acidity, always keep bottles sealed when not in use and consider buying smaller quantities more often.





